How to Document Cost-Effective Maintenance Tasks Part 4: Criticality Analysis
Torbjörn Idhammar, President, IDCON INC
Assessing Risk vs. Consequence and Scoring for Criticality Analysis
Part 4 of this series will cover how to decide what PMs we should document first, and typically we do a criticality analysis.
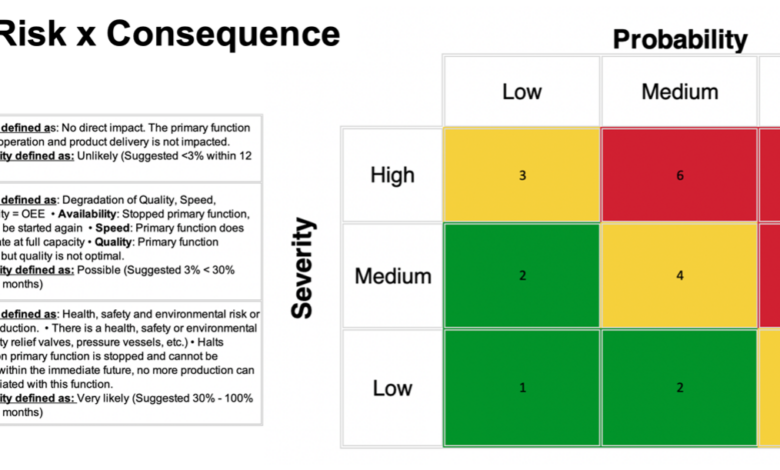
As we like to say at IDCON: Keep it simple. It is best to keep the criticality analysis as simple as possible. As with any type of criticality analysis, the formula is Risk x Consequence. The “risk” represents the probability of the failure or breakdown occurring, and the “consequence” could refer to safety, environmental, high cost, lost production, etc.
Risk vs. Consequence

There should be no more than five levels of scoring in order to avoid confusion and create an efficient criticality analysis process for your organization.
Applying the Criticality Analysis
At IDCON, we find that an effective way to apply the results of a criticality analysis is to look at it purely from a production standpoint. It is useful to use a block diagram for each piece of equipment to assess the consequence of a breakdown, for example how much downtime there will be. This lets you know how sensitive the equipment is from a production standpoint.

Once this is made clear through Preventive Maintenance identification and discussion with the Production team, it can be analyzed through a technical standpoint, for example, the probability of breakdown and what typically causes a breakdown in that equipment.
At this point, multiply cost increase by revenue loss caused by production loss to create a simple algorithm for criticality.
Watch Tor’s video related to this article on our Youtube Channel.
Sign your organization up for IDCON’s Develop and Manage Preventive Maintenance Training today!
Sign your organization up for IDCON’s Develop and Manage Preventive Maintenance Training today! Torbjörn Idhammar is president and CEO of IDCON, Inc. and section editor, Reliability & Maintenance, for Paper360° magazine. Contact him at t.idhammar@idcon.com. For more articles, please visit: www.idcon.comand www.maintenanceworld.com.